Javascript
Table of Contents
- 1. Javascript
- 2. General Purpose
- 3. Limited
- 4. Console
- 5. jsFiddle
- 6. Variables
- 7. Strings
- 8. Lists
- 9. Objects
- 10. Functions
- 11. DOM
- 12. Inspecting the DOM
- 13. Selecting Elements
- 14. Raw vs jQuery
- 15. Modifying the DOM
- 16. Apply CSS style
- 17. Synchronous
- 18. Synchronous Python
- 19. Asynchronous
- 20. Callbacks
- 21. Asynchronous Javascript
- 22. Why Async?
- 23. Event -> Function
- 24. Listen to events
- 25. jQuery
- 26. AJAX
- 27. Infinite Scroll
- 28. jQuery AJAX
- 29. JSON
- 30. Summary
1 Javascript
2 General Purpose
- Javascript full programming language
- Started in the browser
- Now used on servers, command line, devices…
2.1 Spread of Javascript notes
- If it can be written in JS, it will be
- Very lightweight language, lots of reach
3 Limited
- Manipulate the DOM
- Validate form values
- Make asynchronous web requests (AJAX)
3.1 This lecture notes
- We'll just scratch the surface to get a sense of what's possible
- Basics: adding elements and information to the DOM
- Checking values
- Understand asynchronous calling
- Focusing on what makes Javascript unique for the web
4 Console two_col
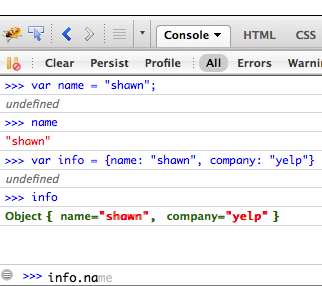
- Firebug or Chrome Tools run Javascript
- Easiest way to play with language
console.logcan print to the log from anywhere
4.1 Demo notes
- Open Chrome Tools, setting variable
- document.getElementsByTagName('IMG')
- assign to variable
- for( var i=0; i<imgTags.length; i++) {console.log(imgTags[i].src);}
5 jsFiddle center
- Write and run HTML, CSS, Javascript
6 Variables
- Declare with
varto scope correctly - Weak, dynamic typing
var a = 3; var b = 5; var c = a + b;
6.1 Typing notes
- What is
c? - Don't worry too much
- Means you can assign whatever you want to a variable name
- Different types can be combined… Javascript tries to do the right thing, but it can be wrong
7 Strings
var a = 'hello '; var b = 'world!'; var c = a + b;
7.1 Quote Char notes
- What is
c? - Single or double quotes, up to you
8 Lists
var l = [1 ,2, "jim"]; l[1];
8.1 Indexed notes
- 0 indexed
- Will return 2
9 Objects
- Similar to Maps or dicts
var titles = { info253: 'Web Arch', info256: 'Applied NLP'}; titles.info253; /* 'Web Arch' */ var schools = { berkeley: {info253: 'Web Arch'}, stanford: {cs101: 'Intro CS'}}; schools.stanford.cs101; /* 'Intro CS' */
9.1 Nested notes
- May be nested
- Any datatypes for values
- Strings for keys
10 Functions
var add = function(a, b) {return a + b;} var c = add(2, 7) /* c is now 9 */ var arithmetic = {add: add, subtract: function(a, b) {return a - b;}}; var d = arithmetic.subtract(11, 4); var e = arithmetic.add(0, 3); /* d is now 7; e is now 3; */
11 DOM animate
- Document Object Model
documentis a Javascript Object- You can modify it and reflect the changes
12 Inspecting the DOM two_col
- You can use
childNodesto explore children - Will return a list
document.childNodes[1]
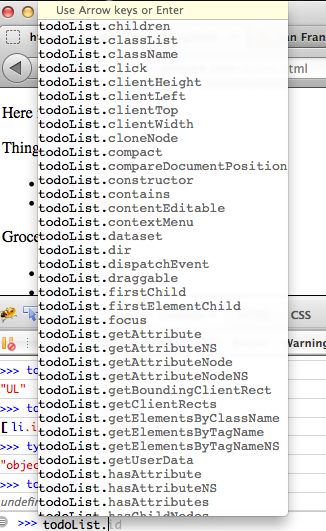
13 Selecting Elements center
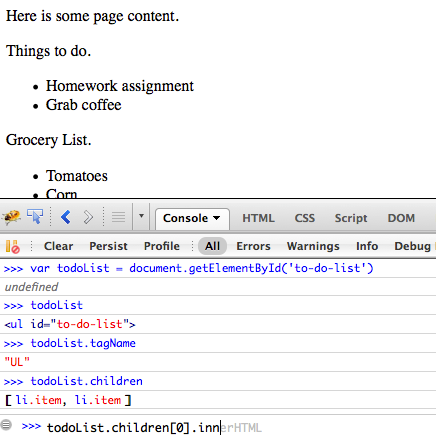
getElementById('target')
14 Raw vs jQuery
/* raw */ document.getElementById('to-do-list'); /* or getElementsByTagName, and getElementsByClassName */ /* jQuery */ $('#to-do-list'); $('#to-do-list li.item');
14.1 Format notes
- What format does the jQuery selector remind you of?
- Automatically selects the right raw Javascript to call
- Trade-off: can be slower, unexpected results
15 Modifying the DOM
.innerHTMLis the text HTML inside the element
- Homework assignment
- Grab coffee
15.1 Modify notes
- use non-slide version
- var todoList = document.getElementById('to-do-list');
- todoList.innerHTML += '<li class="item">Go out for dinner';
16 Apply CSS style
todoList.childNodes[1].style.background = "pink"; /* jquery */ $('#to-do-list .item').css('background', 'green');
17 Synchronous
- Linear execution, waiting for each function to finish
- "End" of a program when all statements executed
- Similar to calling and being on hold
17.1 Never! notes
- Javascript on the page is always responding to the user
- When updating the page, or requesting information from the server, we don't want the whole app to freeze
- Call, on hold (your call is important to us), talk, ask for info, on hold
18 Synchronous Python
file = open("todo.html") content = file.readlines() response = urlopen("http://people.ischool.../todo.html") html = response.read()
18.1 When? notes
- When is the content read? after the file is opened
- When is the http call made? after the file is read
- When is the response read? after the HTTP server request is made
- Almost too obvious that I will have to show the alternative as contrast
- "on hold" while url is being read; nothing else in the program is executing; can't start fetching the URL while waiting for the file to load
19 Asynchronous
- Respond to events independently
- Run functions in response to actions
- "Callbacks" instead of being "on hold"
19.1 Notes notes
- Events include: page scroll, clicking, submitting forms, hovering, page finished loading
- When those events happen, run some function.
- Callbacks an example of this
20 Callbacks two_col
- You want to make a request to your Bank
- Dial their number… on hold (synchronous)
- Or have them call you back? (asynchronous)

20.1 Trade-offs notes
- Wait: don't get confused, context switch
- Wait: but a lot of wasted time, no on else can talk to you
- Call back: frees you up
- Call back: but you have to leave instructions in case they call back and you aren't there
21 Asynchronous Javascript
fs.readFile("todo.html", "utf-8", function(error, data) {console.log(data)}) $.ajax("http://people.ischool.../todo.html", { success: function(data) { $('#ajax-snippet').append(data); } })
21.1 When? notes
- When is the content read? after the file is opened
- DIFFERENCE: When is the request made: Immediately after the readFile is
"kicked-off", does not wait for file to be read
- When is the response read? after the HTTP server request is made
- "Callbacks" are used to handle the result, not inline with code
22 Why Async?
- When do you want your Javascript to "finish"?
- What should UI do while waiting?
- What should UI do while animating?
22.1 Answers notes
- never! Always interacting
- don't freeze!
- still allow other elements to be interacted with
23 Event -> Function
23.1 onclick notes
- Handle click event
hrefof "#" means "don't actually go anywhere"
24 Listen to events
function increment() { var el = document.getElementById("ticker"); el.firstChild.nodeValue += " tick"; } var el = document.getElementById("ticker"); el.addEventListener("click", increment);
tick
24.1 Callbacks notes
incrementfunction is called when the click event happens- when we specify
incrementit is the "callback"
25 jQuery
$("#ticker").click(function() {...});
25.1 Inline notes
- jQuery hides the specific calls needed
- functions can be specified inline, you don't need to declare them
- Although it often helps readability
26 AJAX
- Asynchronous Javascript And XML*
- Allows Javascript to make additional requests
- Why?
26.1 More Info notes
- Gather more information, eg. sophisticated auto complete
- Fill in information in place
- Infinite scroll
- *Actually doesn't use XML much anymore: HTML snippets and JSON
27 Infinite Scroll
27.1 AJAX notes
- When the scroll event or view events happen, javascript will make an AJAX call to server
- Server will respond with HTML inside JSON
28 jQuery AJAX
$('#get-homework').click(function(event) { $.ajax('/snippet', { success: function(data) { $('#ajax-snippet').append(data); event.stopPropagation(); } }) });
28.1 Callbacks notes
- Again, we're using callbacks
- We can't wait around while the server responds: maybe the user is clicking somewhere else!
- Instead we specify what to do when the call returns
- Also callbacks for
error, other conditions
29 JSON
- Pass data as if it were a Javascript Object
- Common data format in a variety of languages
{firstname: "Jim",
lastname: "Blomo",
school: "Berkeley",
jobs: ["Yelp", "A9"]}
29.1 Javascript Object Notation notes
- used in place of XML
30 Summary

- Javascript used to manipulate DOM, CSS styles
- Javascript is a full, asynchronous programming language
- Used to enhance existing, semantic HTML
- Forms used to take input from users, send data to servers
30.1 Next notes
- How do they send data? Upcoming lectures
